Comparison of the features of IO-Link and IO-Link Wireless
We will explain two important technologies that promote the digitalization and smartification of manufacturing sites: IO-Link and IO-Link Wireless. These technologies integrate sensors and actuators on the manufacturing floor into a digital network, enabling real-time data collection, diagnostics, and parameter setting. For example, it becomes possible to monitor and control at the sensor level, which was previously difficult, such as remote monitoring of pressure sensor measurements, predictive maintenance of equipment using vibration sensors, and automatic setting changes according to manufacturing conditions.
Here, we will take a detailed look at the basic features, advantages of introduction, and technical specifications of each.
What is IO-Link?

IO-Link is an industrial communication technology, an open and standardized protocol for connecting sensors and actuators to higher-level systems such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers). This technology was developed in 2006 and standardized as the international standard IEC 61131-9 in 2013.
By introducing IO-Link, it is possible to create a seamless flow of communication and information from the lowest sensor level to the highest information network layer, contributing to the digitalization and efficiency of the entire factory.
IO-Link's Position in Industrial Networks
Industrial networks are generally classified into the following five layers:
| Layer | Contents |
|---|---|
| Information Network Layer | Located at the top level, it manages information for the entire factory or company.Includes core systems such as ERP and MES, and mainly uses standard Ethernet. |
| Control Network Layer | This layer comprehensively controls and monitors each production line and equipment within the factory. Includes SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, and often uses industrial Ethernet protocols (e.g., EtherNet/IP, PROFINET). |
| Controller Level Layer | This is the layer where PLCs and DCS (Distributed Control Systems) that control individual production facilities and machinery are located. Requires high-speed and reliable communication, and industrial real-time Ethernet such as EtherCAT or CC-Link IE are used. |
| Device Level Layer | This is the layer where devices that actually control equipment, such as actuators and I/O devices, are located. Fieldbuses such as PROFIBUS, DeviceNet, and CC-Link are often used, but in recent years, the adoption of industrial Ethernet has also been increasing. |
| Sensor Level Layer | Located at the lowest level, this is the layer where various sensors, switches, etc. are connected. Here, IO-Link plays an important role. |
IO-Link is a communication standard mainly used at the sensor level layer. IO-Link uses point-to-point communication that directly connects sensors and actuators with an IO-Link master, enabling each device to send and receive data individually.
Basic Features
We will explain the basic features of IO-Link from the perspectives of connection method, bidirectional communication, and easy setting and maintenance.
Connection Method
IO-Link is a simple communication method that connects sensors and actuators to higher-level control devices in a one-to-one point-to-point connection. It usually uses 3-wire (Class A (Port Class A) standard) or 5-wire (Class B (Port Class B) standard) unshielded cables, and the connection is as simple as conventional sensor wiring. The communication distance can be extended up to 20 meters, which is sufficient for general industrial applications such as factory production lines.
Bidirectional Communication
It supports bidirectional communication, allowing simultaneous control commands from the controller to the device and feedback from the device to the controller. Process data, parameter information, and diagnostic information can be acquired from sensors and actuators in real time.
Easy Setup and Maintenance
The IO-Link master can automatically save the parameter settings of the device, so when replacing a device, the settings can be transferred to the new device. Even if a device fails, the settings are automatically transferred to the new device after replacement, eliminating the need for manual reconfiguration. Maintenance work, which conventionally required skilled workers, is greatly simplified.
Advantages
We will explain the specific advantages of digitizing industrial field devices, such as reduced wiring man-hours, enhanced diagnostic functions, and compatibility with a wide range of devices.
Reduced Wiring Man-Hours
Conventional sensors and actuators required multiple wires such as power lines, signal lines, and analog output lines, but IO-Link only requires a 3-wire standard unshielded cable, reducing the labor involved in wiring work. This not only reduces the initial investment in equipment in factories but also reduces maintenance costs such as troubleshooting wiring problems, and also enables more compact control panels.
Enhanced Diagnostic Functions
IO-Link devices can monitor detailed diagnostic information such as device operating status, internal temperature, and operating time, enabling early detection of failure signs. Since the error contents of the device itself can be grasped via the IO-Link master, remote diagnosis of the device can be performed via the network. Networked sensor level improves the resolution of remote diagnostics and contributes to downtime reduction.
Compatibility with a Wide Range of Devices
IO-Link is standardized as an international standard (IEC 61131-9) and is compatible with devices from various manufacturers around the world. Users can choose devices relatively freely according to their application and budget, and can build systems without depending on specific manufacturers. In addition, when adding new devices to existing equipment, flexible expansion is often possible regardless of the manufacturer.
CKD's IO-Link Compatible Products
CKD offers a wide range of IO-Link compatible products, from flow and pressure sensors to seating confirmation switches, to support precision measurement and process control.
| Directory | Contents |
|---|---|
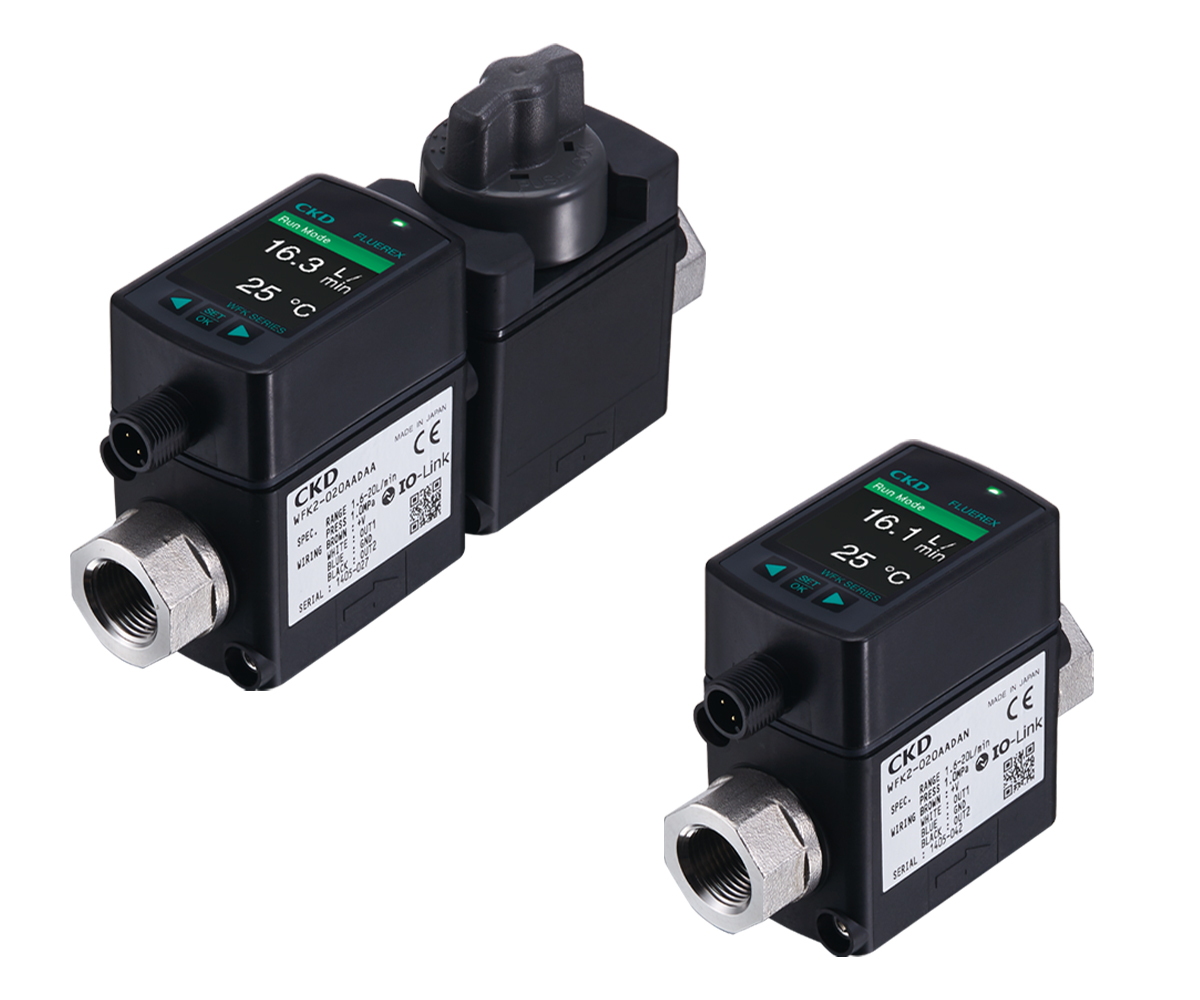 "WFK2 Series" |
・Equipped with digital display screen ・Easy flow rate adjustment |
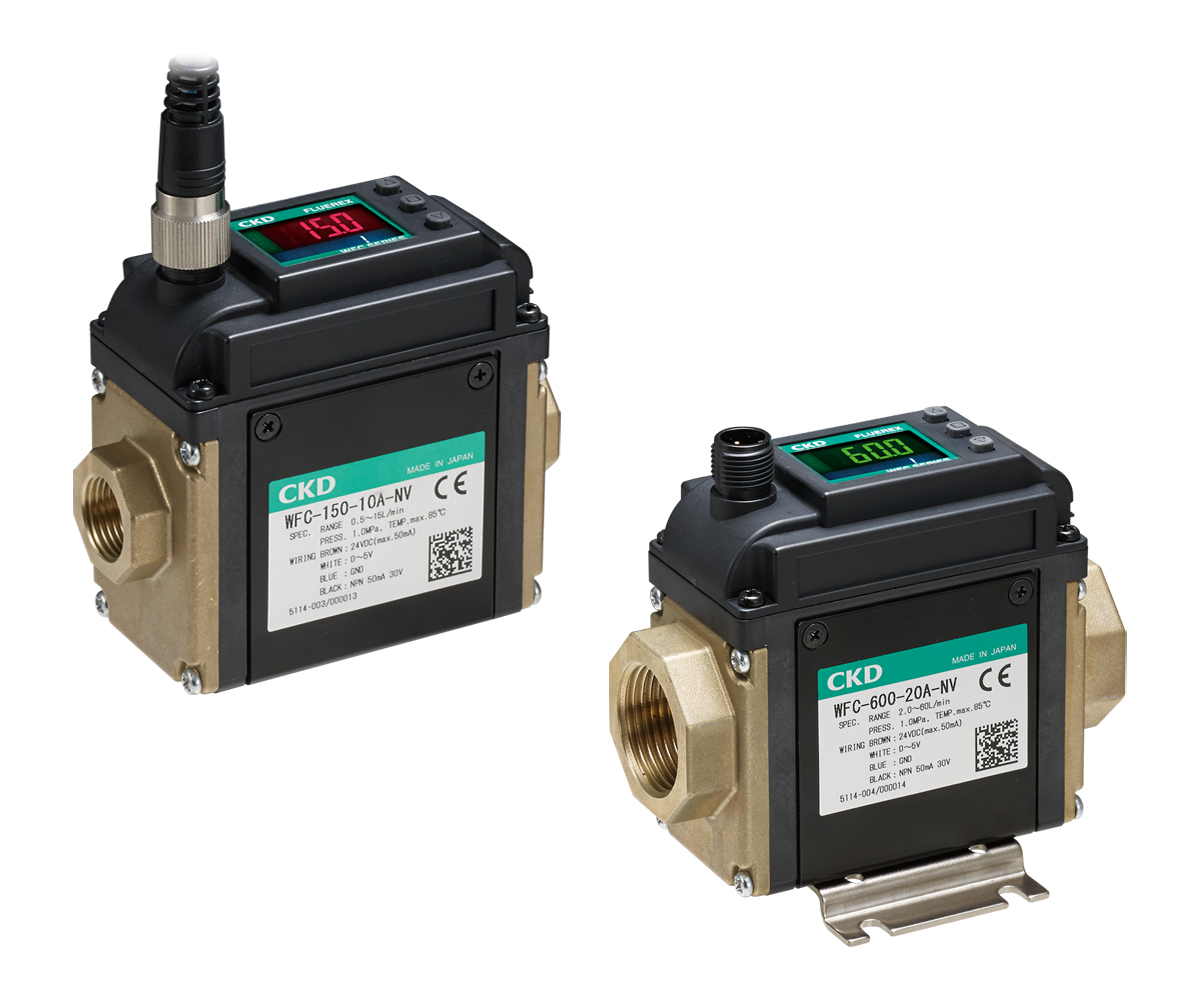 "WFC Series" |
・Water temperature measurement function as standard equipment ・Usable even with poor water quality due to through-structure |
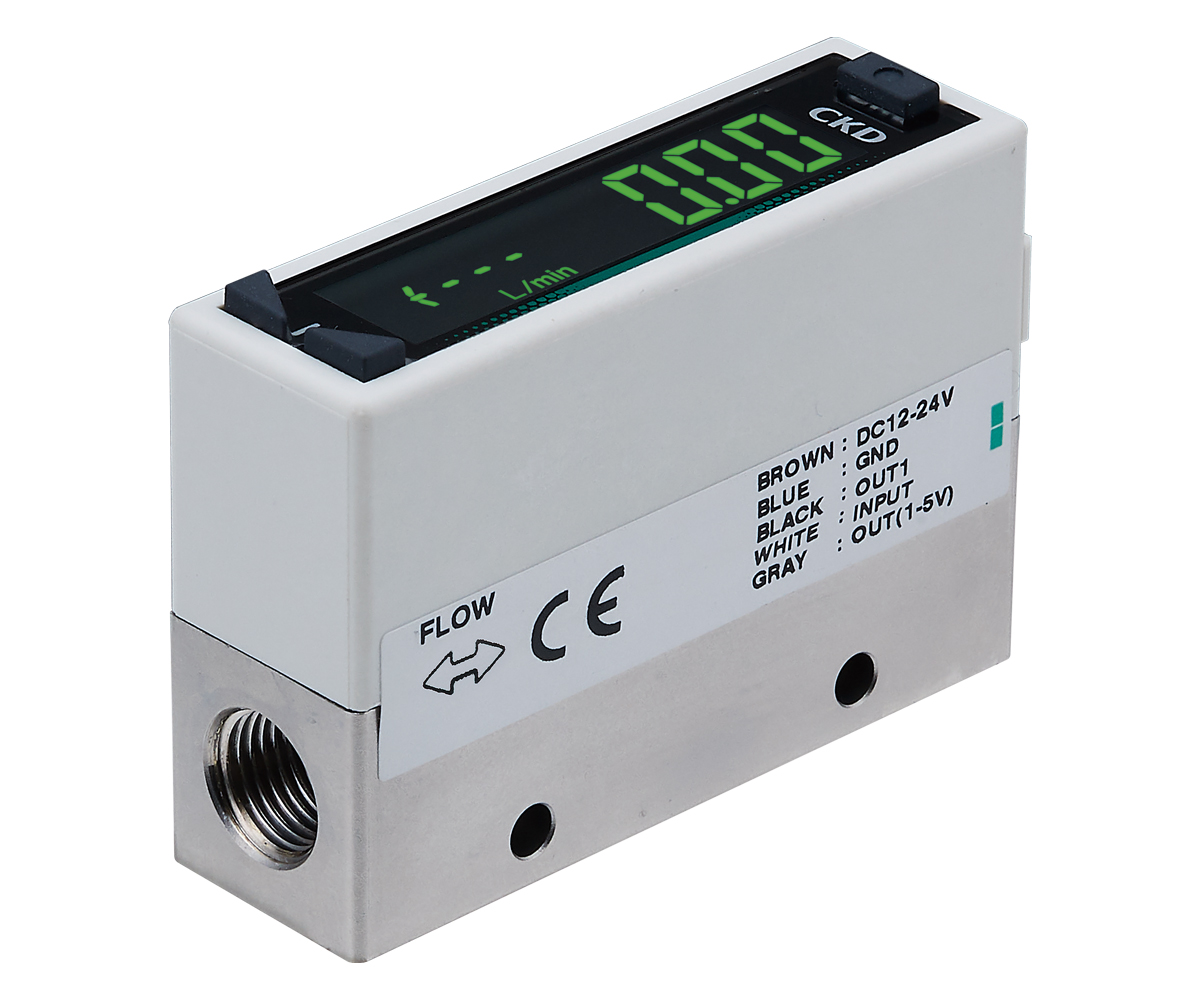 "FSM3 Series" |
・High precision and high response ・Gas type switching function |
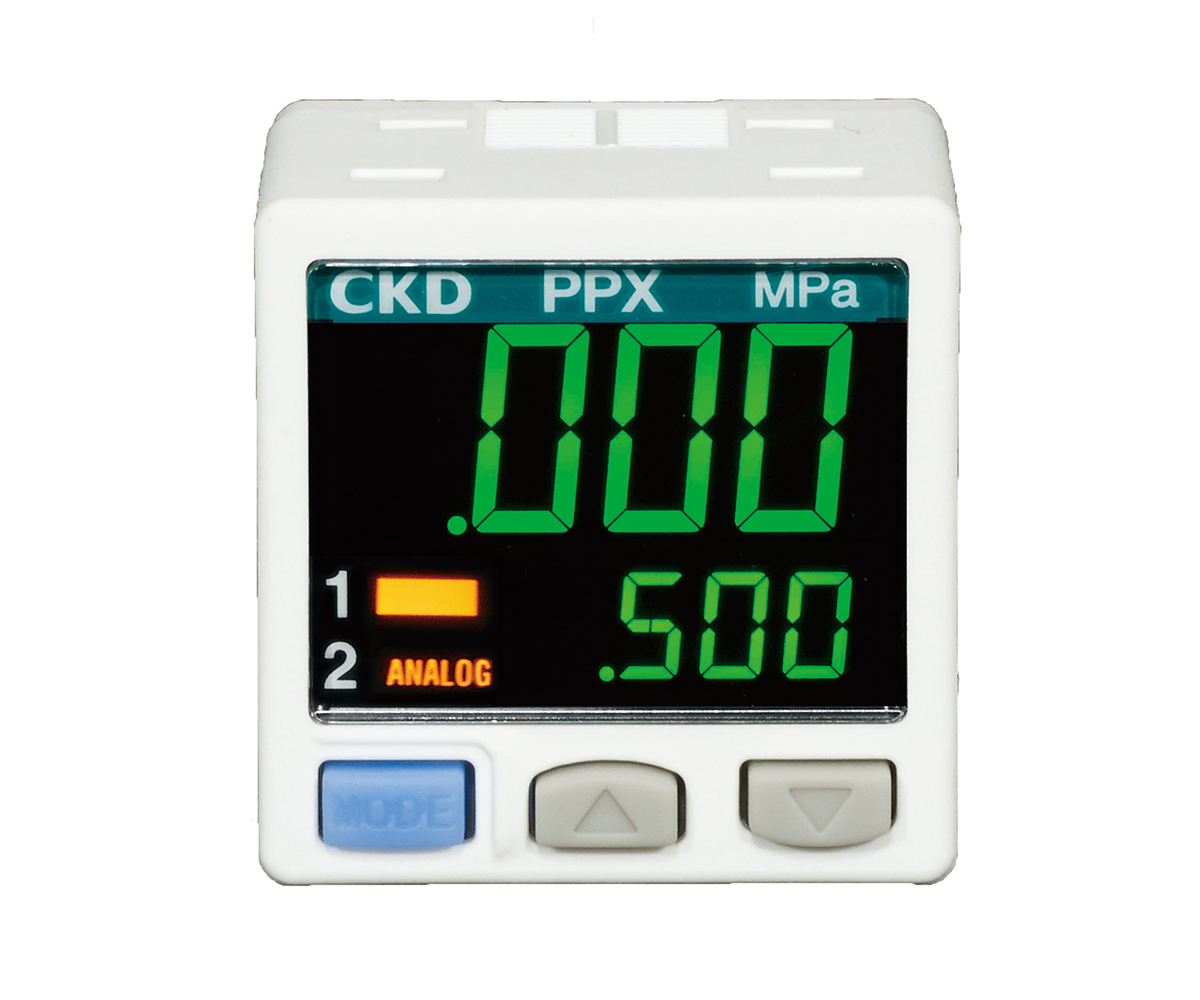 "PPX Series" |
・Compact size ・Settings can be changed while viewing the current value |
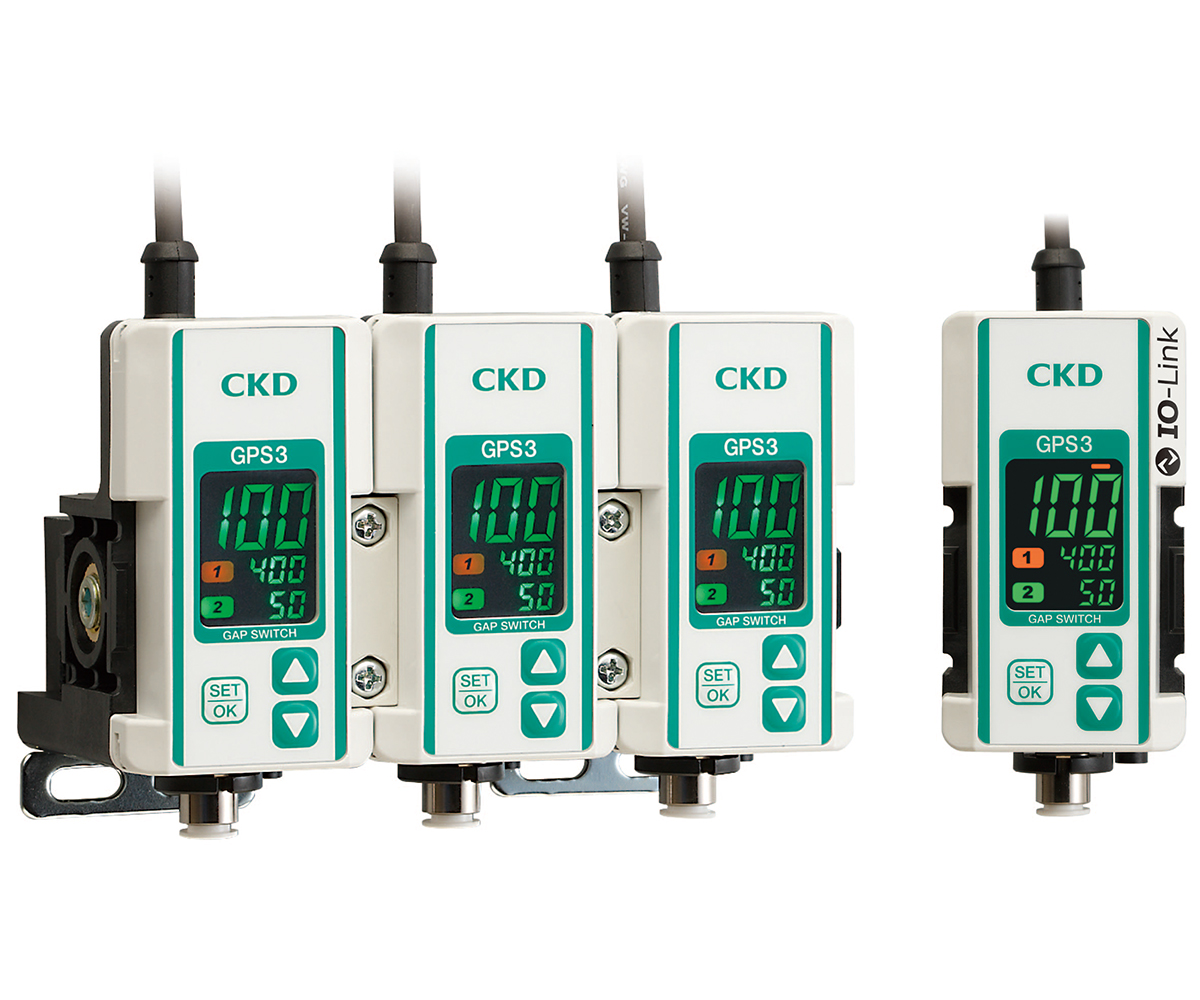 "GPS3 Series" |
・Digital display shows seating status at a glance ・High-precision 2-point output |
For more information about CKD's products and implementation, please contact us.
What is IO-Link Wireless?

The biggest feature of IO-Link Wireless is that it is a wireless communication protocol specialized for industrial applications. Unlike general wireless communication standards, it is designed for use in factory environments, with an emphasis on noise immunity and communication stability.
With IO-Link Wireless, it is possible to connect industrial sensors and actuators to the control system without wiring, which was previously required. In particular, it is expected to be utilized in locations where cable wiring was difficult, such as the tip of robot arms and rotating equipment.
Basic Features
The basic features of IO-Link will be explained from the perspectives of connection method, two-way communication, and easy setting and maintenance.
High Reliability
IO-Link Wireless boasts extremely high reliability with a communication error rate of one in a billion. It adopts a frequency hopping method to prevent radio interference, and maintains stable communication while avoiding interference with other wireless systems. Wireless communication is possible in factory control systems, enabling stable data transmission comparable to wired systems.
Fast Response Time
IO-Link Wireless has a fast communication delay of only 5 milliseconds, allowing you to grasp on-site data in real time. For example, if an abnormality occurs on the production line, it can be detected and dealt with immediately, minimizing the occurrence of defective products.
Flexible Connection
Up to 16 devices can be connected to one master, and periodic data transmission is possible through cyclic communication. The flexible connection configuration enables the construction of an optimal system according to the conditions of the factory production line and equipment.
Advantages
IO-Link Wireless has many advantages over conventional wired IO-Link. Here, we will explain its main advantages.
Wiring Reduction
By using IO-Link Wireless, wiring is significantly simplified compared to conventional wired connections, making installation work easier. It also reduces costs for wiring work and maintenance, and improves flexibility when expanding or modifying equipment.
Utilization in Movable Parts
For moving equipment such as robot arms, rotary tables, and automatic guided vehicles (AGVs), cable breakage due to bending and twisting was a major issue. IO-Link Wireless is wireless, so it eliminates the need for wiring to moving parts and eliminates the risk of disconnection.
Comparison of Technical Specifications
Here, let's compare the main technical specifications of IO-Link and IO-Link Wireless, such as connection method, data transmission speed, and communication method.
IO-Link
Connection Method
The connection method of IO-Link is characterized by a simple and easy-to-use design. To connect the device and the IO-Link master, a 3-wire (Class A (Port Class A) standard) or 5-wire (Class B (Port Class B) standard) unshielded cable is used. Connectors support M5, M8, and M12 standards, but M12 connectors are generally used. (It is also possible to use loose wires such as push-in terminals instead of M-type connectors in terms of communication specifications.)The cable can be extended up to 20 meters, which is sufficient for general industrial applications such as factory production lines.
Data Transmission Speed
IO-Link supports the following three transmission speeds (COM1, COM2, COM3):
・COM1: 4.8 Kbit/s (transmission in 18 ms at the fastest)
・COM2: 38.4 Kbit/s (transmission in 2.3 ms at the fastest)
・COM3: 230.4 Kbit/s (transmission in 0.3 ms at the fastest)
These transmission speeds are selected according to the performance and application of the connected device. The IO-Link master automatically sets the communication speed according to the transmission speed of the connected device.
IO-Link Wireless
Communication Frequency
IO-Link Wireless is a wireless communication standard that uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band (industrial, scientific, and medical band). This frequency band has 80 channels arranged at 1 MHz intervals, and measures are taken to minimize interference with other wireless systems.
Connection Method
supports up to 40 devices (sensors and actuators) with a fast response time of 5 milliseconds for real-time communication. It also supports battery-powered and energy-harvesting sensors, enabling the construction of real-time networks with minimal power consumption.
Data Transmission Speed
In basic data transfer, cyclic communication is performed with a minimum cycle time of 5 milliseconds. This speed satisfies the high-speed response required in industrial applications.
Communication Error Rate
It achieves an extremely high reliability with a communication error rate of one in a billion. This is far superior to general wireless communication standards such as wireless LAN and Bluetooth (error rate of about 1 in 1000). It can be used with confidence even for control system communication, and has reliability comparable to wired systems.
Component Comparison
Here, let's compare IO-Link and IO-Link Wireless from the perspective of components (constituent elements) such as devices and cables.
IO-Link
IO-Link Devices
IO-Link devices include sensors, actuators, switches, valve terminals, RFID devices, and signal lamps. These devices perform digital communication of process data (measurement values and control values), parameter data (setting values), and diagnostic data (device status information) with the IO-Link master.
IO-Link Master
The IO-Link master is an important component that functions as a gateway between IO-Link devices and higher-level communication systems (e.g., PROFINET and EtherNet/IP). It generally has multiple IO-Link ports, and one IO-Link device can be connected to each port.
3-Wire Cable
This is a standard unshielded cable used to connect IO-Link devices and the master. It consists of three wires: L+ (24V power supply), L- (0V), and C/Q (communication/switching signal), and generally uses M12 connectors.
IODD File
The IODD file (IO Device Description) is a standardized XML file that can be called the electronic catalog of an IO-Link device. This file contains detailed information about the device, such as device identification information (manufacturer name, product ID, serial number, etc.), communication parameters, process data structure, diagnostic information, and parameter setting ranges.
IODD files are created in a unified format that does not depend on the manufacturer, so even devices from different manufacturers can be set up and managed with the same engineering tool.
In particular, when replacing a device, the parameters can be automatically transferred to the new device based on the information in the stored IODD file, enabling quick recovery of the equipment.
IO-Link Configuration Tool
The IO-Link configuration tool is a software tool for project engineering and parameter setting of IO-Link systems and devices.
The main functions include:
・Communication control
・Device parameter storage and automatic transfer
・Data exchange with the host system
・Status monitoring and diagnosis
IO-Link Wireless
IO-Link Wireless Master
The IO-Link Wireless master is an important component that plays a central role in the wireless IO-Link system. It manages communication between wireless devices such as sensors and actuators and the higher-level control system (PLC, etc.). Compatibility with conventional wired IO-Link systems is also ensured, and existing IO-Link configuration tools and IODD files can be used as they are.
Wireless Devices
IO-Link Wireless compatible wireless devices include sensors, actuators, and valves. These devices perform wireless communication with the IO-Link Wireless master to exchange process data, parameter data, diagnostic information, etc. in real time.
Communication Channels
IO-Link Wireless uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band (industrial, scientific, and medical band) and has 80 communication channels arranged at 1 MHz intervals. Multipath communication technology minimizes the effects of radio wave reflection and blockage due to metal or walls in the factory, realizing highly reliable wireless communication.(In a space completely shielded by metal, radio waves are also blocked.)
Other necessary components include IODD files and IO-Link configuration tools, but these are the same as those described in the IO-Link section.
CKD's IO-Link Wireless Compatible Products
As a leading company in control equipment, CKD offers IO-Link Wireless compatible products.
| Series | Features |
|---|---|
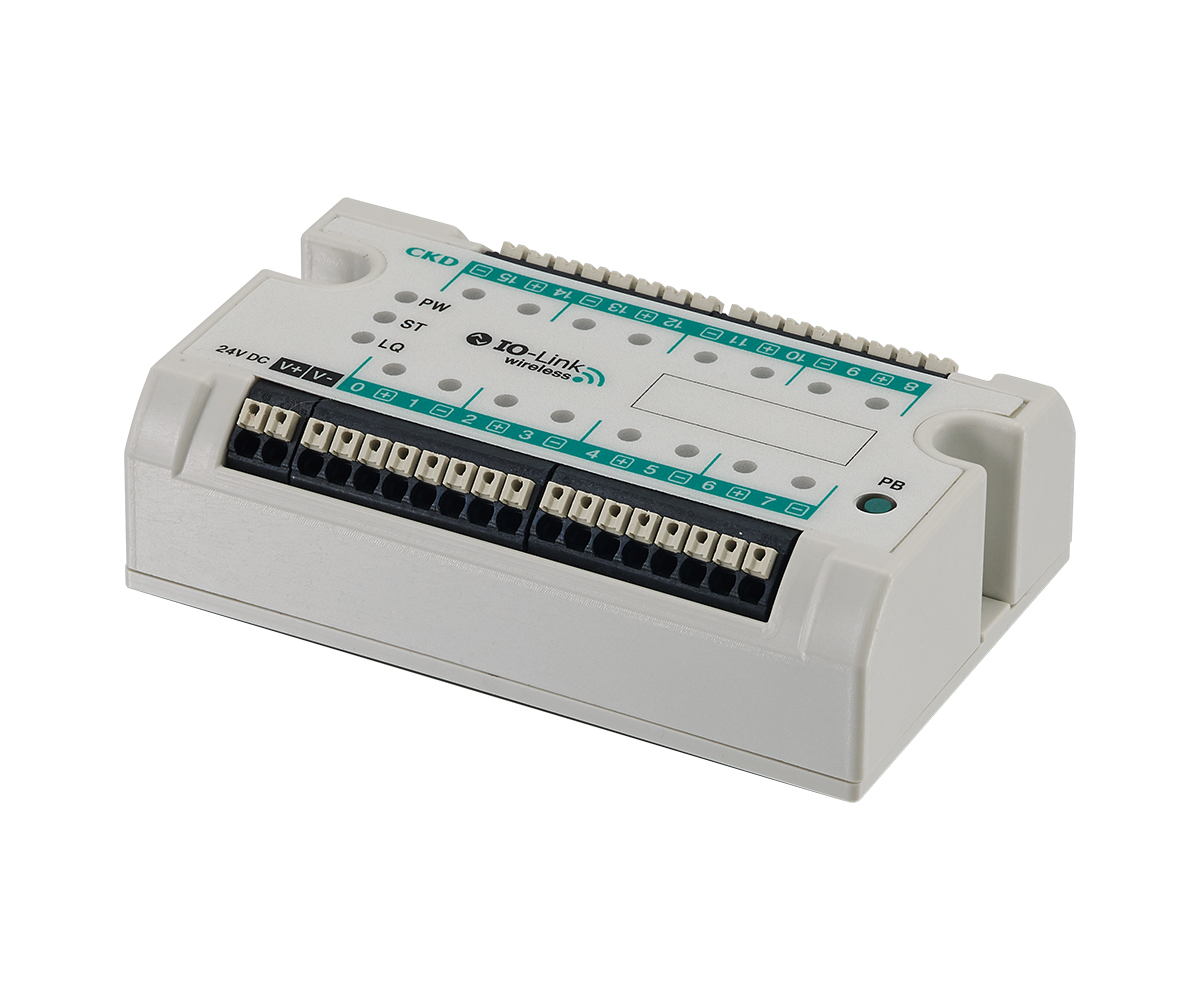 "WD Series" |
・Business card size wireless input unit with 16 digital inputs ・Taking advantage of the characteristics of IO-Link Wireless, it can be used in moving parts such as robot hands and rotary tables. ・Diverse network connections such as EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, and EtherCAT are possible via the IO-Link Wireless master. |
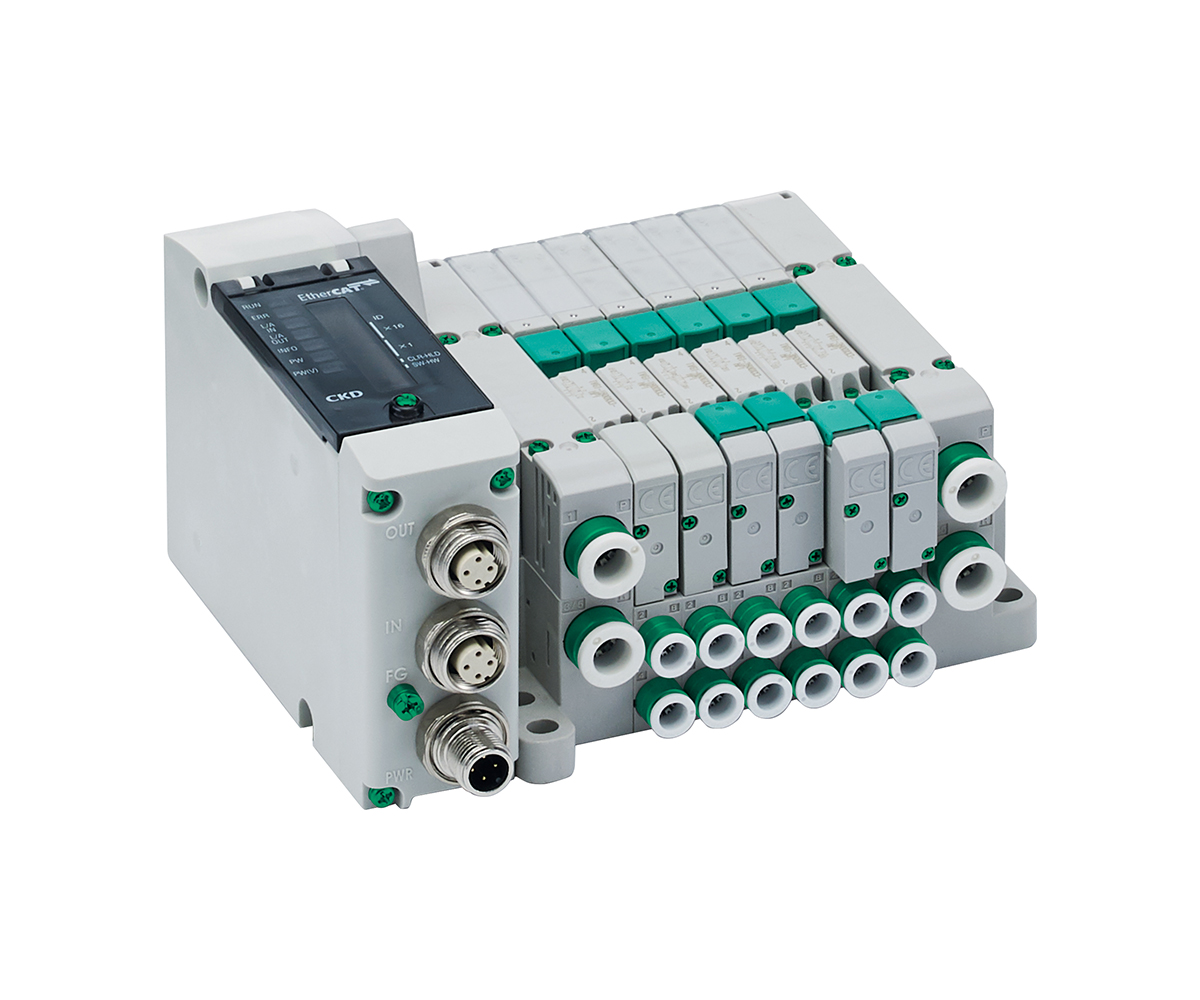 Solenoid Valve Manifold "TVG Series" |
・32 output points ・Can be installed in moving parts. It is possible to add a positioning mechanism in moving parts such as robot hands and rotary tables. ・Durability: 120 million cycles. IP65/67. |
If you have any questions about CKD's IO-Link Wireless compatible products, please feel free to contact our technical consultation desk.