What is an Air Regulator? From Basic Information to Inspection Methods and Troubleshooting
Air regulators are crucial pressure-regulating devices that adjust the supply pressure of compressed air to the required value, ensuring the safety and operational efficiency of industrial equipment. They are used in a wide range of fields, including industrial equipment, construction sites, and food processing. This article provides detailed information on the role and basic functions of air regulators, selection methods, maintenance points, and troubleshooting.
- 1.What is an Air Regulator?
- 2.Main Components of an Air Regulator
- 3.Information Required for Selecting an Air Regulator
- 4.Air Regulator Inspection and Maintenance Methods
- 5.Causes and Remedies for Trouble (Troubleshooting)
- 6.Industries and Fields Where Air Regulators are Used
- 7.Differences Between Air Regulators and Electro-Pneumatic Regulators
- 8.CKD Air Regulators
- 9.Related Pages
What is an Air Regulator?
An air regulator (pressure-reducing valve) is a device that adjusts the pressure of compressed air and reduces it to a specific pressure.Its main role is to reduce the high-pressure air supplied from an air compressor to the appropriate pressure for various air-powered devices.

Basic Functions
Air regulators have two main important functions.
Pressure Reduction
Air regulators have the function of reducing high-pressure compressed air to a predetermined pressure.
In manufacturing sites, compressed air supplied from a compressor is distributed to various air-powered devices.
The compressed air supplied from the compressor is at high pressure, but air-powered devices have a predetermined pressure resistance and are not necessarily compatible with high pressure. Excessive pressure can damage equipment and reduce the efficiency of the entire system.Therefore, it's necessary to adjust the pressure to within the maximum operating pressure range of the devices used on the secondary side, such as cylinders and valves.
For example, even if the compressed air supplied from the compressor is 0.7 MPa, using an air regulator to reduce the pressure to the device's recommended range, such as 0.5 MPa, allows the air-powered device to operate safely and optimally.
Pulsation Suppression
Stabilizing the flow of compressed air maximizes the performance of the equipment.
Compressed air from a compressor may be accompanied by pulsations (pressure fluctuations) during supply, which can lead to instability in the thrust of air cylinders and shorten the lifespan of equipment.The regulator serves to suppress these pulsations. Air regulators have the function of reducing high-pressure compressed air to a predetermined pressure.
Even when pressure adjustment is not required, it is recommended to use a regulator to supply air at a stable pressure.
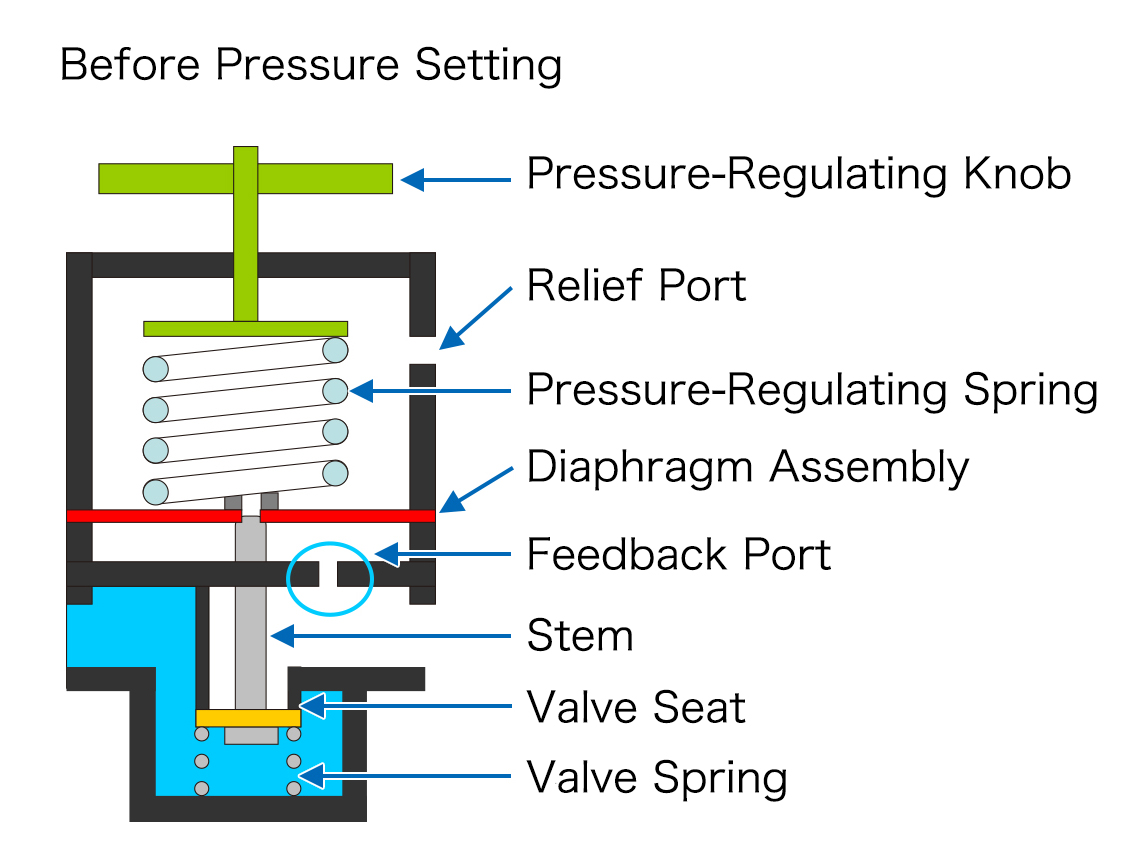
Main Components of an Air Regulator
An air regulator is made up of several components. The main components are as follows.
| Part Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Pressure Adjustment Knob | This is the manual control for adjusting the pressure. |
| Relief Port | This is a port for releasing excess pressure to the outside when the secondary pressure exceeds the set value. Some regulators do not have a relief port. |
| Pressure-Regulating Spring | This spring adjusts the opening and closing of the valve seat. |
| Diaphragm Assembly | A diaphragm is a thin membrane. The outflowing compressed air acts on the diaphragm assembly, and by balancing the force with the pressure-regulating spring, the pressure is accurately controlled. Also, when the adjustment knob is loosened, the diaphragm assembly rises due to the secondary pressure, and excess air is discharged to the outside through the relief port. |
| Feedback Port | The pressure on the secondary side is transmitted to the diaphragm assembly through the feedback port. The diaphragm assembly maintains pressure balance with the set spring force. |
| Stem | Also known as a valve stem, it is a rod-shaped component that directly opens and closes the valve or transmits its movement. |
| Valve Seat | The surface that the valve contacts when it is sealed. It plays a very important role in ensuring that the valve closes tightly and prevents fluid from leaking. |
| Valve Spring | This is a spring used to close the valve. |
Information Required for Selecting an Air Regulator
When selecting an air regulator, you need to know the following information.
Check Pressure Conditions
It is necessary to confirm the primary pressure (high pressure) and the secondary pressure (low pressure). Select an air regulator with a pressure range that can accommodate the pressure required by the air-powered device being used.
Grasp the Flow Rate
Accurately determine the flow rate required by the air-powered device or system being used. For example, if a particular air-powered device requires 300 L/min of air, you need to select a regulator that can handle that flow rate.
Environment and Temperature
The environment in which the regulator is used varies, such as whether it is used indoors or outdoors, in an environment where dust is generated, or in an environment where grease is undesirable. For example, in high-temperature or low-temperature environments, it may be necessary to specify the material. Choose the regulator considering the temperature range, material, and functions of the operating environment.
Check Piping Size
Regulators may have different sized threads at the inlet and outlet. It is necessary to select a size that matches the piping being used.
Pressure Gauge Type
The presence or absence of a pressure gauge is also an important factor. There are two types of pressure gauges: analog and digital. Also, by combining a pressure switch as needed, the system can be controlled when the set pressure is reached. Choose the most suitable type for your application.
Other Functions
If functions or accessories are required for a specific application, select appropriate products and options according to the operating environment and purpose, such as a regulator with a filter, a precision regulator, a bracket, or fittings.
Air Regulator Inspection and Maintenance Methods
Regular inspection and maintenance are essential for long-term use of air regulators.
Perform inspection and maintenance after stopping the supply pressure and confirming that there is no residual pressure.
Inspection Frequency
Regular inspection and maintenance are essential for long-term use of air regulators.
| Guidelines for Inspections | Details of inspection |
|---|---|
| Daily Inspection (Once per day) |
・Operation Check
Before using this product, check that it is operating normally. |
・Lubricator Oil Drip Amount
Insufficient dripping can cause lubrication problems in the target object. |
|
| Regular Inspection (At least once every six months) |
・Check for leaks from piping.
Leaks from piping can lead to problems such as pressure drops, reduced energy efficiency, and increased risk of equipment failure. |
・Check for cracks, scratches, or other deterioration on the main unit.
If cracks, scratches, or other deterioration are found, replace the part with a new one as it may cause damage. |
|
・Check if the filter element is clogged (*Filter-regulator only)
Clogging of the element causes performance degradation. The frequency of problems varies depending on the environment and frequency of use. Therefore, start with a short inspection interval at first and set the inspection cycle while observing the situation. |
Drain Discharge (*Filter-regulator only)
Moisture (drain) accumulated on the secondary side can flow in and cause equipment malfunction, so it is necessary to drain it regularly. Especially in high-humidity environments, it is necessary to increase the frequency of drain discharge or select a product with an auto-drain.
For lubricators, replenish oil regularly so that the oil level does not fall below the lower limit.
Causes and Remedies for Trouble (Troubleshooting)
If it does not operate as intended, it is necessary to inspect according to the table below.
| Malfunction | Cause | Remedy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drain comes out immediately after startup | The amount of drain exceeds the upper limit | Drain the drain | |
| Used exceeding the maximum processing flow rate | Replace with a model that supports the used flow rate | ||
| Drain does not discharge even when the drain cock is opened | Foreign matter is clogged in the drain port | Stop the compressed air, remove the bowl assembly, and clean the inside of the bowl If cleaning does not improve the problem, replace the bowl assembly |
|
| With auto-drain, the drain is not automatically discharged, or air leaks from the drain port | The auto-drain is malfunctioning or clogged with debris | ||
| Air leaks from the bowl mounting area | The O-ring for the bowl seal is scratched or has foreign matter adhering to it | Stop the compressed air, remove the bowl assembly, and clean or replace the O-ring with a new one. | |
| The bowl is damaged | Stop the compressed air, remove the bowl assembly, and replace the bowl assembly with a new one | ||
| When primary pressure is applied, there is air leakage from the gap between the cover and the knob | IN and OUT are connected in reverse | Correct the mounting direction | |
| Pressure does not rise | Insufficient primary pressure | Check the primary pressure | |
| The bowl with the long or restricted primary piping is damaged. | Shorten the primary side piping or increase the pipe diameter | ||
| Pressure gauge needle does not move | The pressure gauge may be faulty, so replace it with a new one | ||
| Pressure does not drop | Back pressure is applied to the regulator | Check if there is a problem with the system | |
| Non-relief type, so it does not relieve | Change to a relief type product | ||
| Leakage occurs from the cover, The set pressure rises abnormally |
Debris is attached to the valve, The diaphragm is damaged |
Clean or replace parts | |
| Secondary pressure pulsates | Pulsation may occur depending on piping conditions and usage | Use with reduced primary pressure or restrict the piping | |
Industries and Fields Where Air Regulators are Used
Air regulators are used in various fields.
Industrial Equipment such as Manufacturing
Many industrial devices on factory production lines operate using air pressure. These devices cannot perform to their full potential without a stable pressure supply. Air regulators help these devices operate stably by adjusting pressure and suppressing pulsations.
Food Processing
In food processing equipment, air regulators also maintain a constant fluid pressure, stabilizing the manufacturing process and creating an environment where the equipment can operate efficiently.
In addition to driving food processing equipment, air regulators are used for conveying food containers, air blowing, adding air to food, and in the nitrogen filling process to prevent oxidation.
Construction Industry
Many tools such as impact drivers and air dusters, and equipment such as pneumatic drifters and pneumatic hammers are used at construction sites. In order for these devices to operate stably, it is necessary to maintain the required pressure. Air regulators play this role in pressure adjustment.
Differences Between Air Regulators and Electro-Pneumatic Regulators
Air regulators adjust pressure manually or mechanically and have a relatively simple structure suitable for general pressure control.
On the other hand, an electro-pneumatic regulator is a device that electronically controls pressure according to an input signal, enabling highly accurate and flexible control.
Electro-pneumatic regulators are equipped with feedback control that operates according to the difference between the input signal and the signal from a built-in pressure sensor. Because the pressure can be automatically adjusted based on the deviation between the input signal and the actual pressure, it is particularly effective in production facilities where multi-product production and high functionality and accuracy are required.
Furthermore, electro-pneumatic regulators are also suitable when it is required to change the air flow rate.
CKD Air Regulators
CKD offers a wide range of air regulators, from basic models to high-performance types.
For precision machining at manufacturing sites, you can choose a high-precision type, and for use outdoors in harsh environments, you can choose an outdoor specification series. We also have a lineup of products that meet on-site requirements, such as compact models that save installation space, and series for food factories.
CKD provides total support from before to after product introduction. Specialists who know the field inside and out will lead you to solutions for your problems.
For detailed product information, please check CKD's air regulator product list.
Contact us today for a consultation.
Related Pages
The internal check valve of the reverse regulator allows the pressure on the secondary side (OUT side) to be quickly discharged to the primary side (IN side). Therefore, it is suitable for cases where standard regulators such as balancers cannot sufficiently expel secondary side pressure or when exhaust capacity greater than what a relief valve can provide is required.
When mounting filter-regulators or regulators, checking the pressure can be difficult because the pressure gauge is facing the opposite side due to the difference in flow direction. CKD regulators can resolve this issue by removing the pressure gauge and changing the installation surface.